
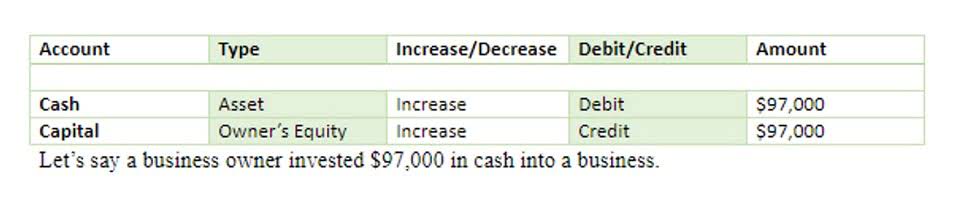
In a situation where the company provides goods and services for which the cash is to be received at a future date, the revenue is recorded immediately without waiting for the time when the cash will be collected. It is recorded by debiting accounts receivable and crediting revenue. Where a company receives cash in advance for which goods or services are to be provided at a future date, it initially debits cash and credits unearned revenue (also known as prepaid revenue). Unearned revenue is a liability that is subsequently converted to earned revenue when the related goods or services are provided to customers. It is done by debiting unearned revenue (or prepaid revenue) and crediting revenue.
Revenue Recognition Methods and Timing
The revenue recognition principle is key to following GAAP, making financial statements clear for stakeholders. This must meet strict conditions like proving a contract exists and the actual delivery of goods or services. The revenue recognition principle states that revenue should be recognized and recorded when it is realized or realizable and when it is earned. In other words, companies shouldn’t wait until revenue is actually collected to record it in their books. Revenue should be recorded when the business has earned the revenue. This is a key concept in the accrual basis of accounting because revenue can be recorded without actually being received.
Payment
Proper revenue recognition affects the income, balance, and cash flow statements. Performance obligations are commitments to deliver goods or services to a customer. These obligations must be distinct, meaning they can balance sheet be separately identified and provide value to the customer. Determining distinct obligations involves examining contract terms and the nature of the goods or services. Manual revenue recognition prone to errors and can be time-consuming, especially for businesses with complex contracts or high transaction volumes.
Transaction Matching

The transaction price reflects more than just the raw cost of the delivered goods or services. It also accounts for and defines any potential fees, return policies, financing options, or discounts that might be applied to the transaction. This new guidance, in turn, established a more neutral, industry-agnostic process for recognizing revenue no matter the type of business being evaluated.

In theory, investors could line up the financial statements of different companies to assess their relative performance more accurately. Variable consideration includes discounts, rebates, refunds, and performance bonuses. Statistics and case studies highlight the need for accurate revenue recognition. These scenarios stress the importance of following rules and maintaining vigilant revenue recognition. It meant learning new rules and checking old contracts carefully to follow the new model.

Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations
According to the matching principle, expenses should be recognized in the same period as the related revenues. according to the revenue recognition principle If expenses are recorded as they are incurred, they may not match the revenues that they relate to. If an expense is recognized too early, the company’s net income will be understated. If an expense is recognized too late, a company’s net income will be overstated.
Recognize revenue when (or as) the performance obligation is satisfied
For instance, revenue from a service contract might be recognized over time, while revenue from a product sale is recognized when the product is delivered. By selling one doll, John earns $75 in cash and records the revenue immediately. This transaction has all of the same elements as above, but this time, the collectability must be determined because the sale was made on credit. John knows that his customer has the ability to pay and the intent to pay. Therefore, the collectability is probable, and John should recognize revenue in the current period.
Case Study 2: Revenue Recognition in a Construction Project
- If these criterion cannot be met, the recognition must be deferred until it can be met.
- A low A/R balance implies the company can collect unmet cash payments quickly from customers that paid on credit while a high A/R balance indicates the company is incapable of collecting cash from credit sales.
- For example, if one of your customers enters bankruptcy and is expected to be dissolved, you wouldn’t recognize any outstanding invoices for this business as revenue.
- This has shortened revenue cycles from 24 to 18.7 months (page 2 of the PDF).
- Outlined in Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606, it states that revenue should be recognized when goods or services are delivered, not just when payment is received.
- This approach makes financial reports more consistent, reliable, and easy to compare.
And if it’s not done perfectly, your business can legally end up in hot water. Companies must meticulously follow GAAP to provide reliable financial information that facilitates informed decision-making and maintains trust in the financial markets. Even though Mike is actually paying the expense in February, it needs to be recorded in January. Mike debits ‘utility http://www.caraycecaonline.com.ar/2021/08/25/calculate-the-change-in-working-capital-and-free/ expense’ to increase his expenses and credits accounts payable to increase the amount he owes.
